SMC MODELS
TAA-induced acute liver failure model
The TAA-induced acute liver failure model
The TAA-induced acute liver failure model (Thioacetamide) represents a widely used model for the evaluation of drugs against acute liver failure. While TAA itself is not hepatotoxic, its reactive metabolites covalently bind to proteins and lipids thereby causing oxidative stress, inflammation and centrilobular necrosis.
A single shot of TAA is administered intraperitoneally to 7-weeks old, female C57BL/6J mice which then develop severe and acute liver injury in just 24h. This model is particularly useful for the pharmaceutical drug evaluation of drug candidates against acute liver failure.
As a positive control in this model, we suggest to use Bortezomib, which is a proteasome inhibitor. The treatment with Bortezomib demonstrated significant alleviation of TAA-induced liver damage.
Comparison of different acute liver failure (ALF) models
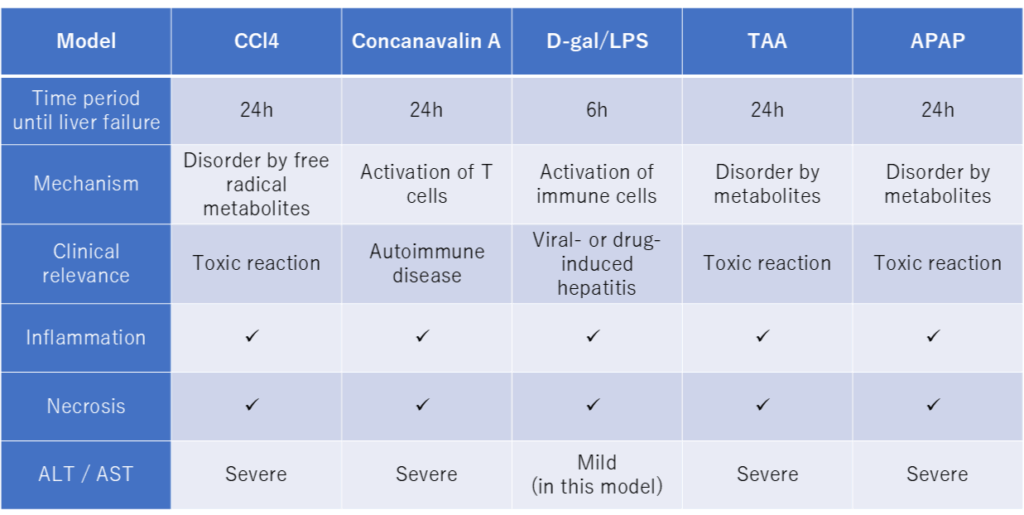
For a more in-depth information on each model feel free to check out our other ALF models:
CCl4 Acute Liver Failure Model
D-gal/LPS Acute Liver Failure Model
Concanavalin A Acute Liver Failure Model
APAP Acute Liver Failure Model
Analysis items and key endpoints of the TAA-induced acute liver failure model
Histopathological analysis
HE Staining for evaluation of necrosis / inflammation
Immunohistochemistry
For different molecular markers
Biochemistry analysis
ALT
AST etc.
Gene expression analysis
TNF-α
IL-6 etc.
Cytokine analysis
TNF-α
IL-6 etc.
Contact us
We would be happy to get the chance to discuss your needs regarding the pharmacological evaluation of your drug compound against acute liver failure and to introduce our capabilities with you. So, if you are interested in more information or in talking to us, please use the contact button below to reach out to us.
