SMC MODELS
SSc-ILD model
The SSc-ILD model
The SSc-ILD model is a commonly used disease model for the pharmacological efficacy evaluation of new drug candidates against Systemic Sclerosis with Interstitial Lung Disease. Systemic sclerosis is a chronic connective-tissue disease of unknown cause and characterized by fibrosis of the skin and other internal organs such as the lung.
30-50% of SSc patients shows the onset of the SSc-ILD, and 25 % of SSc patients develop the severe pulmonary dysfunction within 3 years of SSc diagnosis making it a major complication among SSc patients. Furthermore, in SSc-ILD patients (extensive disease), the survival rate decreases compared with SSc patients without ILD (limited disease).
How we create the SSc-ILD model
To create the SSc-ILD model, we inject 1.0mg/mL Bleomycin in a volume of 50µL subcutaneously every other day into the pre-shaved back of 7-weeks old, female C57BL/6J mice for 4 weeks. The injection sites are located at the corners of a 1.5 cm2-square shaved area and used in rotation (1→2→3→4…).
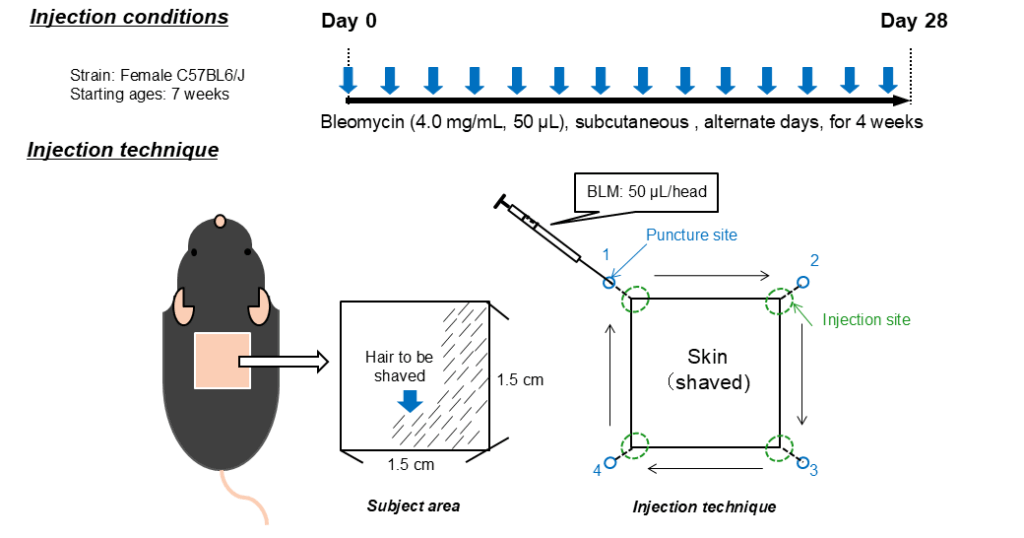
To minimize the effect of needle puncture on the skin to be collected for samples, puncture site and injection site are separated.
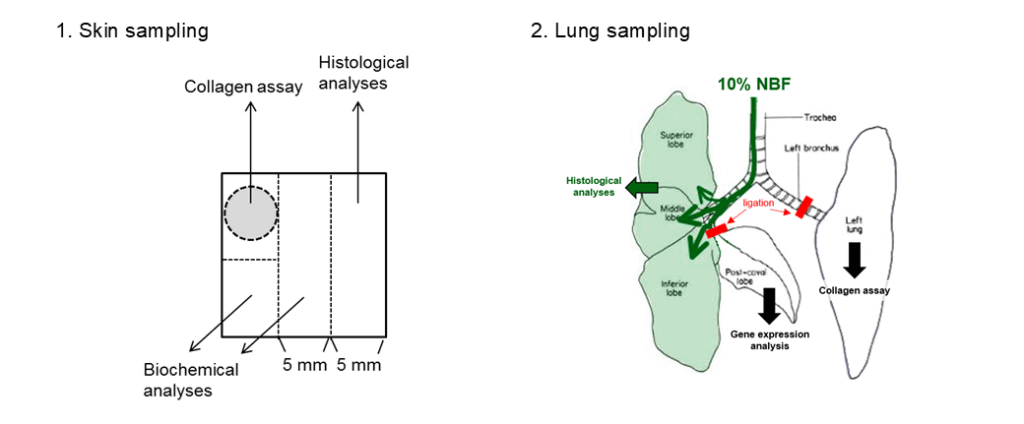
A 5-mm circle is clipped using a dermal punch and used for collagen quantification. The remaining intact area is cut out into 3 rectangles, one for histology and two for biochemical analyses.
The left and post-caval lobe bronchi are ligated to avoid leakage of the instilled fixative. Three fixed lobes (for histological analyses) and two unfixed lobes (for gene expression analysis and collagen assay) are harvested from each mouse.
Analysis items and key endpoints
Histopathological analysis
HE staining (relative dermal thickness, relative adipose layer thickness)
Masson Trichrome staining (relative fibrosis area, Ashcroft score)
Alpha SMA staining
Biochemistry analysis
Sircol Collagen Assay (skin collagen content)
Hydroxyproline content
Other parameters
Body weight
Nintedanib as reference control compound
Nintedanib is an inhibitor of tyrosine kinases, which showed vascular remodeling and antifibrotic, anti-inflammatory effects. The compound demonstrated improving effects in the SSc-ILD model and showed a tendency to improve relative dermal thickness, skin fibrosis as well as lung fibrosis.
Nintedanib has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of interstitial pulmonary fibrosis, but is also used for the treatment of patients with Systemic Sclerosis without interstitial lung disease. For more information, please also check out our Bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis model (SSc w/o ILD).
ALK5 inhibitor as reference control compound
ALK5 inhibitor II is a cell permeable, potent, selective and ATP-competitive inhibitor of TGF-β RI kinase. The compound showed significant improving effects in skin fibrosis and an improving trend in the Ashcroft score.
Tofacitinib citrate as reference control compound
Tofacitinib citrate is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. It blocks the activity of Janus kinase enzymes, which are involved in inflammatory pathways. The compound shows significantly improving effects in skin collagen content, relative dermal thickness, relative fibrosis are and an improving trend in the Ashcroft score.
Nintedanib, ALK5 inhibitor and Tofacitinib citrate have been validated in our SSc-ILD model and either of them can be used as reference drug in your study to compare the pharmacological efficacy with your drug candidate’s.
