SMC MODELS
Bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis model
The Bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis model
Bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis model is a well-characterized disease model for skin fibrosis and commonly used for studying biological pathways of Systemic Sclerosis (SSc). Systemic sclerosis is a chronic connective-tissue disease of unknown cause and characterized by fibrosis of the skin and internal organs.
The model encompasses key pathophysiological features of SSc: Epidermal hypertrophy and dermal fibrosis, which makes this model attractive for a simple proof-of-concept study for SSc, or in vivo screening for anti-fibrotic molecules.
How we create the Bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis model
Bleomycin is subcutaneously injected every other day into the pre-shaved back of mice. The injection sites are located at the corners of a 1.5 cm2-square shaved area and used in rotation (1→2→3→4…). We administer 1.0mg/mL Bleomycin in a Volume of 50µL for 4 weeks, every other day.
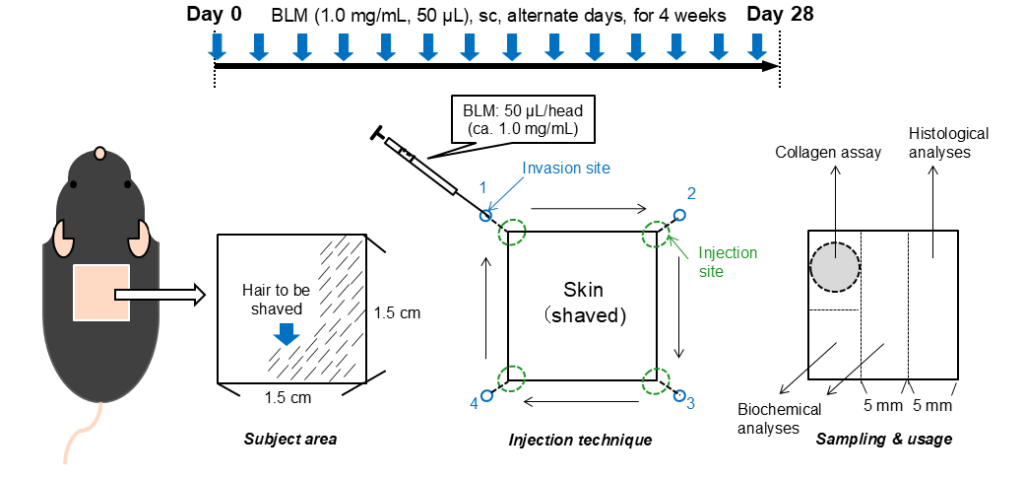
After sacrifice, a 5-mm circle is clipped using a dermal punch and used for collagen quantification. The remaining intact area is cut out into 3 rectangles, one for histology and two for biochemical analyses.
Analysis items and key endpoints
Histopathological analysis
HE staining (relative dermal thickness, relative adipose layer thickness)
Masson Trichrome staining (relative fibrosis area)
CD3-positve staining
Biochemistry analysis
Sircol Collagen Assay (skin collagen content)
Other parameters
Body weight
Imatinib mesylate as established reference control compound
Imatinib mesylate is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor against c-Abl, PDGFR, and several other tyrosine kinases. C-Abl is crucial for induction of ECM proteins through the TGF-b pathway, its inhibition reduces the synthesis of EMC components. Imatinib interferes with PDGF signaling by blocking the tyrosine kinase activity of PDGFR. The administration of Imatinib has shown a significant improvement in relative dermal thickness and can therefore be used as reference control in your pharmacological efficacy study.
Nintedanib as established reference control compound
Nintedanib is an inhibitor of tyrosine kinases, which was shown to have antifibrotic, anti-inflammatory, and vascular remodeling effects. It was thoroughly tested in our facilities for the improvement effects on the Bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis and showed a tendency to improve relative dermal thickness as well as skin fibrosis.
Nintedanib has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of interstitial pulmonary fibrosis, but is also used for patients with SSc-ILD.
For more information, please also check out our SSc-ILD model.
