SMC MODELS
APAP-induced acute liver failure model
The APAP-induced acute liver failure model
The APAP-induced acute liver failure model (Acetaminophen) makes use of the over dosing effects of this widely used antipyretic and analgesic drug. An overdose of APAP can cause severe liver damage resulting in ALF. Although the main portion of acetaminophen is metabolized in the liver through glucuronidation and sulfation and then excreted via urine, approximately 10-15% of APAP is metabolized in hepatocytes by cytochrome P450 into a highly toxic metabolite thereby leading to hepatocyte necrosis.
A single shot of high dosed APAP is administered intraperitoneally to 10-weeks old, male C57BL/6J mice which leads to acute liver failure inflicted by metabolic by-products within 24h after administration.
Comparison of different acute liver failure (ALF) models
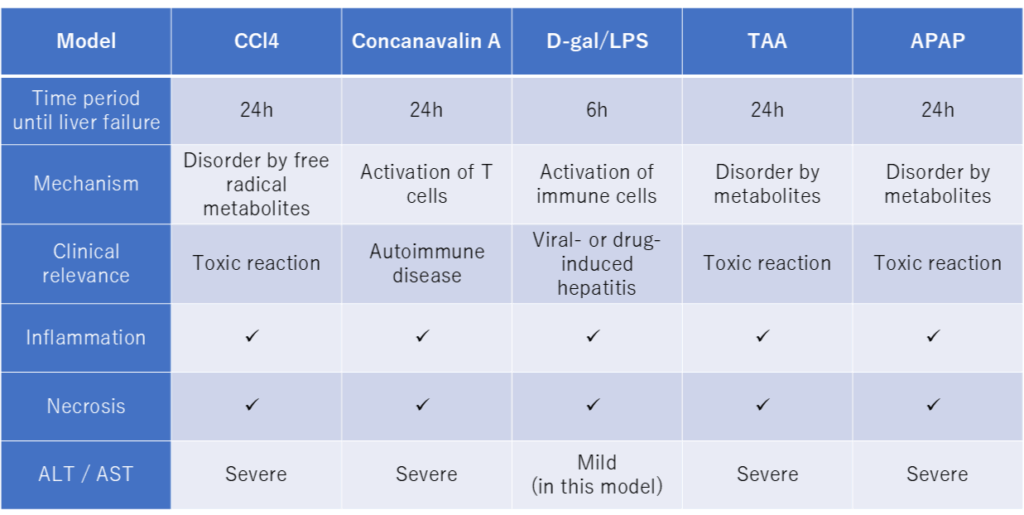
For a more in-depth information on each model feel free to check out our other ALF models:
CCl4 Acute Liver Failure Model
D-gal/LPS Acute Liver Failure Model
Concanavalin A Acute Liver Failure Model
Analysis items and key endpoints
Histopathological analysis
HE Staining for evaluation of necrosis / inflammation
Immunohistochemistry
For different molecular markers
Biochemistry analysis
ALT
AST etc.
Gene expression analysis
TNF-α
IL-6 etc.
Cytokine analysis
TNF-α
IL-6 etc.
Contact us
We would be happy to get the chance to introduce our preclinical study capabilities and discuss your needs regarding the pharmacological evaluation of your drug compound against acute liver failure. Therefore, if you are interested in talking to us for to receive more information, please use the contact button below to send us an inquiry.
