SMC MODELS
Adriamycin-induced nephropathy model
Adriamycin-induced nephropathy model for CKD
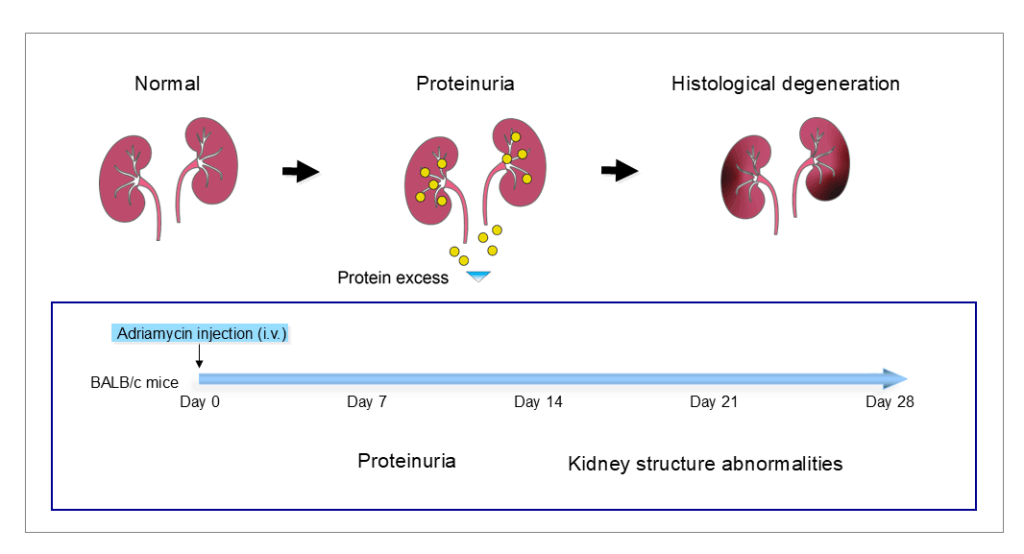
The Adriamycin-induced nephropathy model is a well-characterized model that can be used for pharmacological drug evaluations of early to mid-disease progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD). The model mirrors human CKD caused by primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS).
How we create the Adriamycin-induced nephropathy model
We create the Adriamycin-induced nephropathy model by injecting Adriamycin intra venous into BALB/c mice on day 0 and run the model for 28 days, with a treatment period of 21 days starting on day 7. In the course of disease progression, the model shows proteinuria as well as kidney structure abnormalities such as podocyte injury followed by glomerulosclerosis, tubulointerstitial inflammation and fibrosis.
Analysis items and key endpoints
Histopathological analysis
PAS staining (tubular injury index, glomerulosclerosis)
Sirius Red staining (for collagen deposition / fibrosis)
Biochemistry analysis
Serum Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Serum creatinine
Urine Albumin-to-creatinine ratio
Urine NGAL
Other parameters
Body weight change
Kidney weight
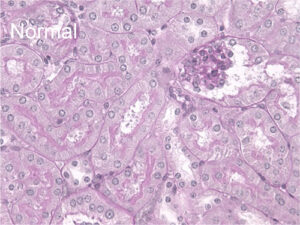
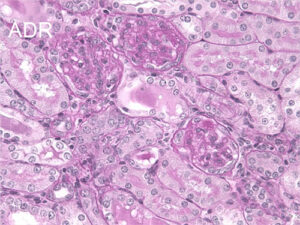
Figure 1. ADR model, image of a PAS stained kidney
Compared to normal mice, the ADR model shows increased mesangial substrate.
Valproic Acid (VPA) as established reference control compound
Valproic Acid (VPA) is a histone deacetylase inhibitor and has anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic properties. In the Adriamycin-induced nephropathy model VPA has been shown to attenuate proteinuria and kidney Injury. We have used VPA as reference control in a number of studies using this model and have seen improving treatment efficacy in Serum BUN, NGAL, tubular injury index and kidney fibrosis.
Other CKD Models
For the pharmacological efficacy evaluation of drugs against CKD and AKI,
we also offer the following models:
Adenine Model
Folic Acid Model
